The Center for X-Ray Optics is a multi-disciplined research group within Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory's (LBNL) Materials Sciences Division (MSD). Notice to users.
Precision optical coatings for soft
x-ray and EUV applications.
"Multilayer films are a vital component of many EUV and soft x-ray optical systems. We strive to improve on existing multilayer technologies while exploring and developing new systems for research and commerical applications."
Eric Gullikson,
Principal Investigator


Multilayers make EUV and soft
x-ray reflection possible.
Traditional refractive lenses don't work with x-ray and EUV light because absorption is too high. To bend and focus light at these wavelengths, optical systems must employ reflective or diffractive lenses. However, to be reflective to x-rays and EUV light at normal incidence, mirrors need special coatings called 'multilayers' that contain alternating layers of materials only a few atoms thick.
Tailor-made to the application.
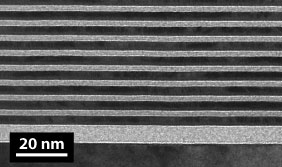
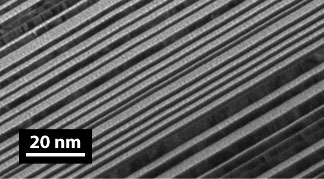
By tailoring layer thicknesses and overall structure, the reflectivity and optical properties can be customized for many applications. In order to work with high efficiency, and maintain the correct phase of the reflected light, layer thicknesses have to be reliably controlled to the level smaller than the width of a single atom.
Attosecond.
Multilayers can be designed to reflect different frequencies at different depths, enabling attosecond pulse compression. They can also be designed to reflect broadband light using an aperiodic layer structure (shown to the left).
Pioneering the field for 25 years.
CXRO has been making, testing and utilizing multilayer x-ray mirrors since 1984. CXRO has made major contributions to understanding the physics and chemistry of these devices, and to their utilization in optical systems for a variety of research fields, including x-ray astronomy, plasma spectroscopy, x-ray lasers and synchrotron radiation research.

